FFT in Multiple Dimensions#
We can extend our FFT to more than one dimension. Consider the 2-d case:
\[\begin{align*}
F_{k_x,k_y} &= \sum_{m =0}^{N_x - 1} \sum_{n=0}^{N_y -1}
f_{mn} e^{-2\pi i (k_x m/N_x + k_y n/N_y)} \\
&= \sum_{m =0}^{N_x - 1}
e^{-2\pi i k_x m/N_x}
\underbrace{\sum_{n=0}^{N_y -1} f_{mn} e^{-2\pi i k_y n/N_y}}_{\mbox{this is the y transform}}
\end{align*}\]
We see that we can decompose the multi-dimensional transform into a sequence of one-dimensional FFTs.
Example: FFT of my dog#
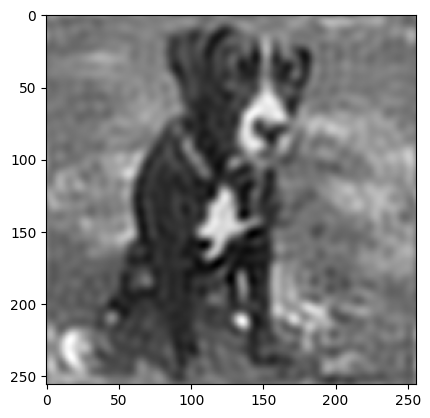
Here’s an image of my dog:

download: luna_bw.png
Let’s take the FFT. We’ll use the built in NumPy FFT routines.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
First let’s read the image in as an array
f = plt.imread("luna_bw.png")
f.shape
(256, 256)
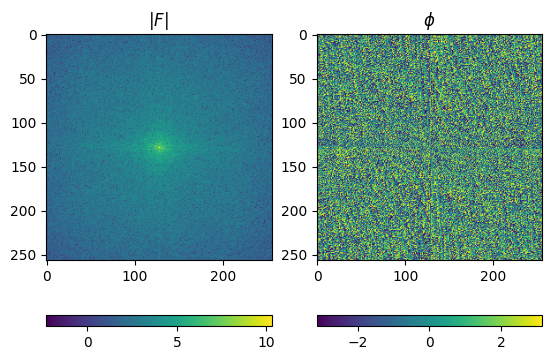
Now let’s take the FFT
F = np.fft.fft2(f)
We can shift the spectrum so the k = 0 wavenumbers are at the center, using numpy.fft.fftshift()
F_shift = np.fft.fftshift(F)
Now we can plot the amplitude and the phase (which we can get from numpy.angle()
F_mag = np.abs(F_shift)
F_phase = np.angle(F_shift)
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121)
im = ax1.imshow(np.log(F_mag))
ax1.set_title(r"$|F|$")
fig.colorbar(im, ax=ax1, orientation="horizontal")
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122)
im2 = ax2.imshow(F_phase)
ax2.set_title(r"$\phi$")
fig.colorbar(im2, ax=ax2, orientation="horizontal")
<matplotlib.colorbar.Colorbar at 0x7fc0b8776510>
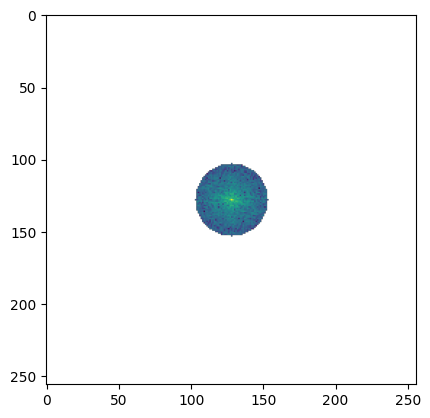
Let’s filter out high frequencies
ix, iy = np.mgrid[0:F_shift.shape[0], 0:F_shift.shape[1]]
ix -= F_shift.shape[0]//2
iy -= F_shift.shape[1]//2
F_filtered = F_shift.copy()
F_filtered[np.hypot(ix, iy) > 25] = 0.0
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.imshow(np.log(np.abs(F_filtered)))
/tmp/ipykernel_4182/1388428532.py:2: RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in log
ax.imshow(np.log(np.abs(F_filtered)))
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7fc0b82fb890>
Let’s transform this back and see the result
f_filtered = np.fft.ifft2(np.fft.ifftshift(F_filtered))
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.imshow(f_filtered.real, cmap="gray")
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7fc0b81e56d0>